Neuroanatomy Basics:¶
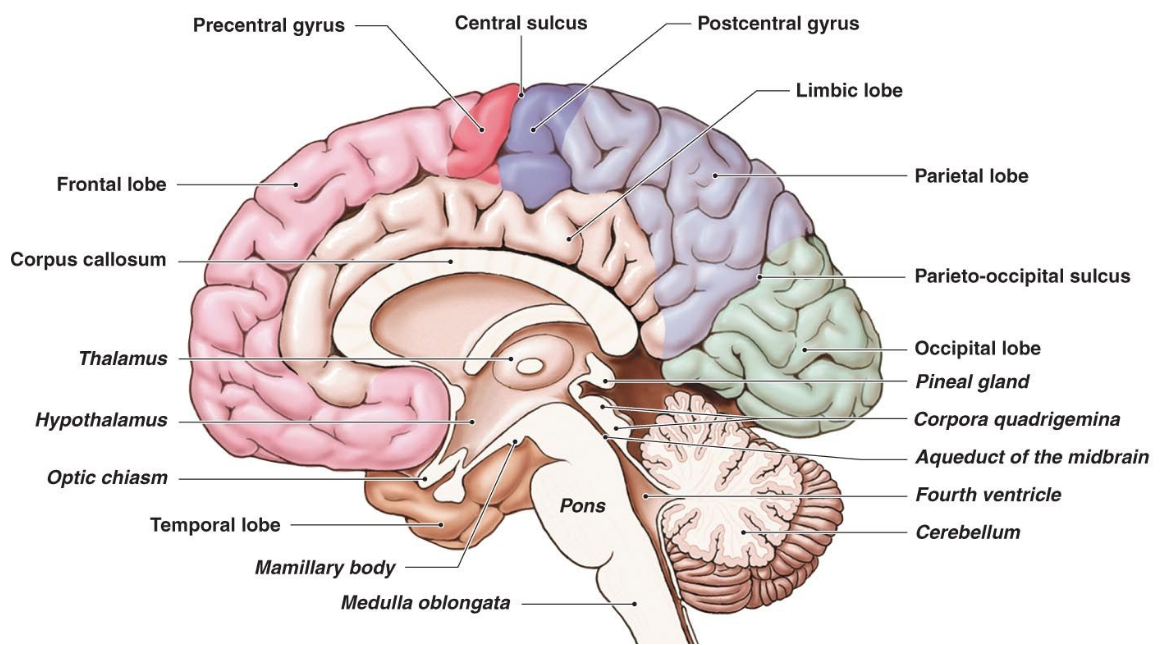
- Cerebral Cortex — consists of the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe. Responsible for thought, reasoning, coordinated movement, language, visual processing
- "Cortex" is latin for "bark"
- Cerebellum — responsible for balance
- "Cerebellum" is latin for "little brain"
- Thalamus — responsible for relaying sensory information to or from the cerebral cortex
- Hypothalamus — responsible for regulating body temperature, emotions, hunger, thirst and circadian rhythms
Limbic System:¶
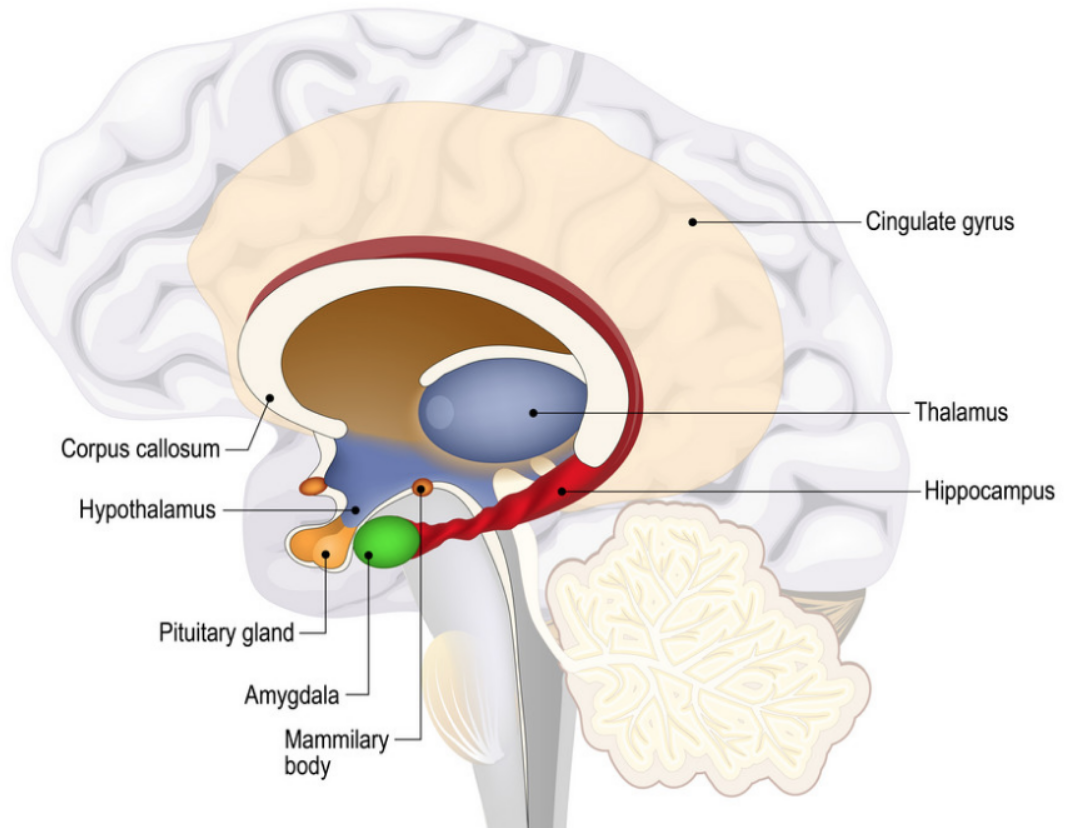
Limbic system — responsible for emotions and memory, primarily
- Amygdala — responsible for lower-level emotional responses such as fear or aggression
- Hippocampus — reponsible for 'transferring' short-term memory to long-term memory
- Mammillary bodies — responsible for recall memory
- Cingulate cortex — responsible for linking motivational outcomes to behaviour, for example
- Basal Ganglia — responsible for habit formation
Neurons:¶
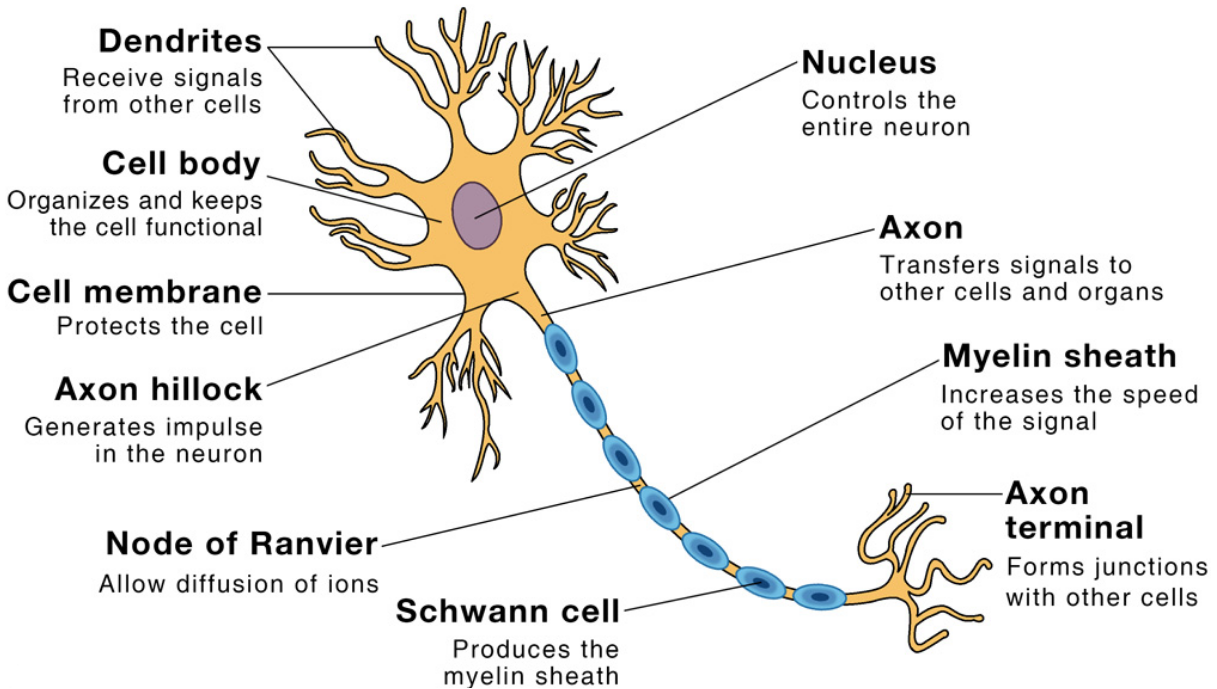
Neurons are cells comprising the nervous system which can propagate signals through an electrochemical process.
- The brain consists of ~100 billion neurons which an average of 10000 synapses for each neuron
- Dendrites — receives input signals from other neurons
- Axons — outputs a signal to the dendrites of other neurons
Synapse¶
- Synapse — an electrochemical junction
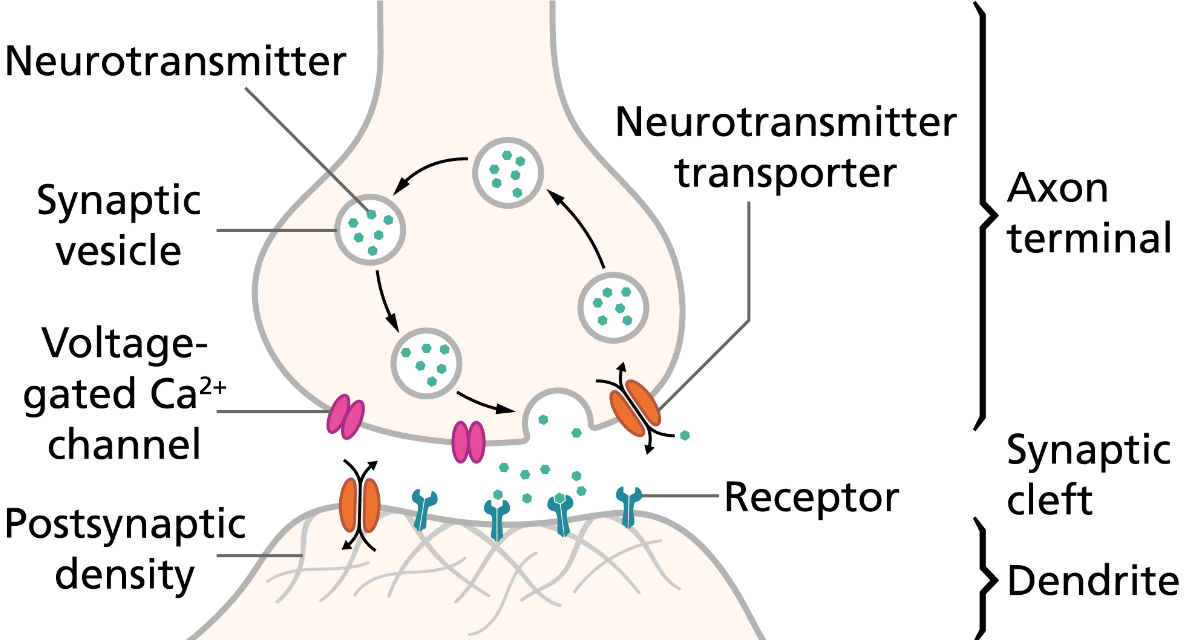
- Synaptic vesicle — a 'capsule' of neurotransmitters that are released across the synaptic cleft when the vesicle fuses with the axon terminal's membrane